Asia to North America West Coast schedule sees reliability improvement
Global shipping schedule reliability improved in May 2024, especially on the Asia to North America West Coast, but the Asia to North America East Coast and Asia-Middle East routes showed significant decline.

Global schedule reliability improved 3.8 percentage points month-over-month in May 2024, reaching a yearly high of 55.8%. However, compared to the same period last year, schedule reliability decreased by 11.0 percentage points. This is a trend also seen on commercial routes, where 29 routes decreased compared to the same period last year. Of the five routes that recorded improvements, the Asia to North America West Coast (NAWC) route recorded the most significant improvement.
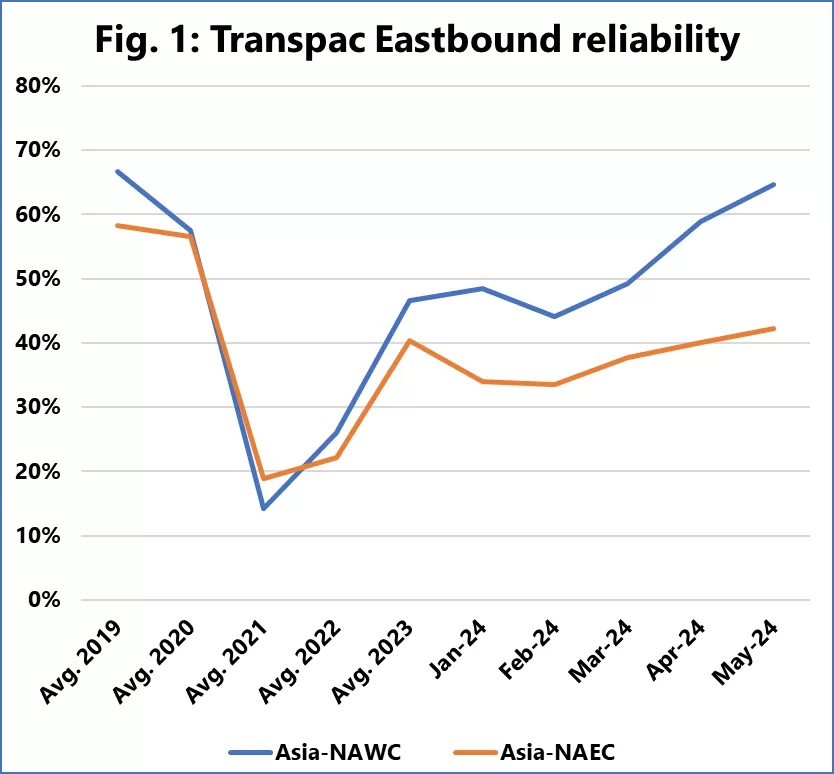
Schedule reliability on the Asia to North America route (Source: Sea-Intelligence)
Figure 1 shows the evolution of schedule reliability for this trade, not only at the monthly level for 2024 but also the average full-year reliability over the period 2019-2023. Additionally, Figure 1 also shows the performance of the Asia to North America East Coast (NAEC) route, as commercially the two routes are closely linked.
While the Asia-NAWC service has improved significantly and is even approaching - but not quite reaching - its pre-pandemic average performance, the Asia-NAEC service has not shown the same improvement. The performance gap between the two trade routes, which began to widen in 2023, is only getting worse.
This means that North American importers using the East Coast route are increasingly facing much greater supply chain disruptions than if they had routed goods through the West Coast.
Among trade routes that underperformed in May 2024, the Asia-Middle East trade saw one of the largest year-on-year declines. Compared to the full-year 2019 average, this trade saw the largest decline in schedule reliability, falling below its pandemic lows. This shows that the Red Sea crisis is indeed having a strong impact on schedule reliability in the region.
See more:
- SITC VIETNAM – LEADING NEW TRENDS
- International shipping and logistics market update - Week 28/2024
- Sea-Intelligence identifies growth of non-alliance services
- CMA CGM ship lost 44 containers off coast of South Africa
Source: Phaata.com (According to Sea-Intelligence)
Phaata.com - Vietnam's First International Logistics Marketplace
► Find Better Freight Rates & Logistics Services!